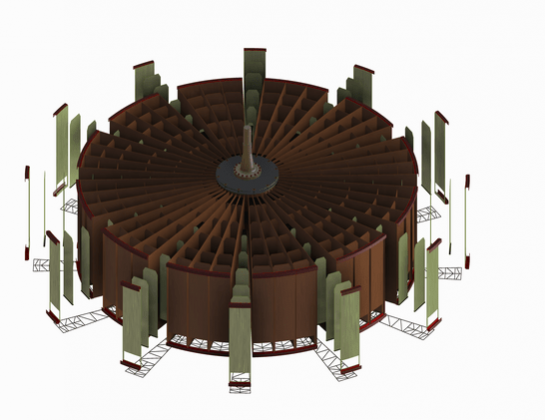
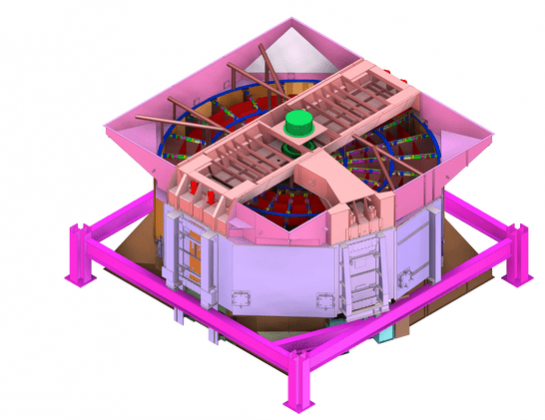
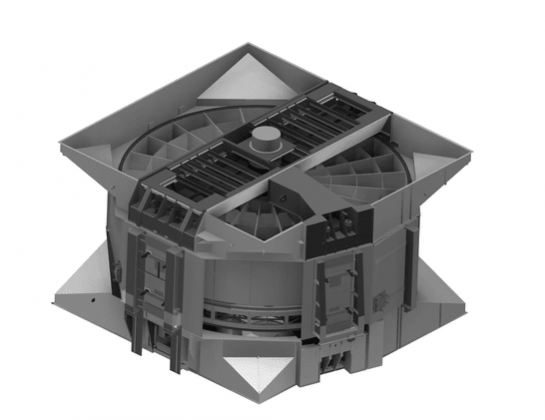
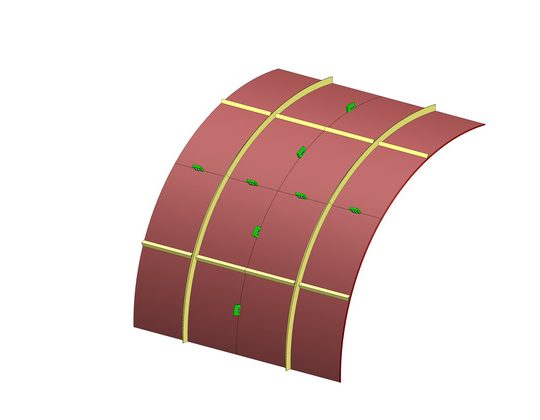
Thermal Power Plant Boilers
Boilers are used in a power plant in order to produce high pressure steam, which is then used to generate electricity. The process through which the steam is produced in a boiler is known as the Rankine cycle. The boiler uses fuels such as coal, natural gas, or nuclear to convert water into steam.
The design of a boiler plays a very important factor in a power plant’s efficiency. Better design means a lower fuel requirement, lower costs and lower emission of pollutants. The study and innovation of boilers is useful because although they are very efficient, their waste products create some of the world’s major pollution problems by emitting greenhouse gases.
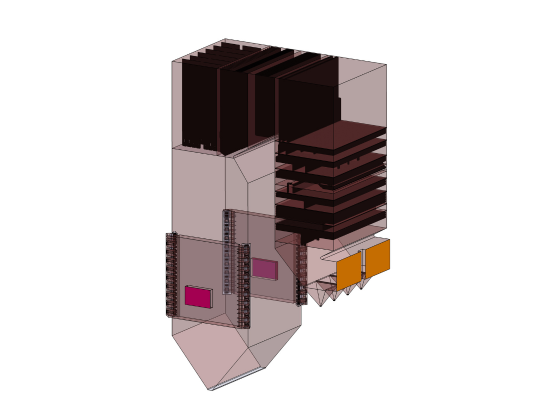
Air Preheaters
In general, a preheater is a heat exchanger that increases the temperature of inlet gas or liquid in any process. An Air-Preheater does this specifically for air, taking energy from steam to heat incoming air elsewhere in the system. By increasing the inlet temperature at which the air enters the process, it improves the overall efficiency of the system.
Air preheaters are being configured into two major different varities based on its Design and process:
- Gas to Air
- Liquid to Air
Ducts
Ducts are conduits or passages used in various applications where air or gas or its equivalent needs to be transferred from one place to another, for example HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) to deliver and remove air. Ducts commonly deliver ventilation air as part of the supply air. Designing a duct system is also called ductwork, which includes the parameters like planning the overall position layout, sizing, optimizing, detailing and finding the pressure losses through a duct system.
Guide Vanes
Guide vanes are sheet metal devices inside of mechanical duct work used to smoothly direct air inside a duct where there is a need to change the direction, by reducing resistance and turbulence; thus improving the efficiency of the flow of air or its equivalent which enhances the desired output. The efficiency of guide-vane design and that of the flow are directly proportional.
Superheaters And Reheaters
Super heaters are one of the most important accessories of a boiler which improves the thermal efficiency. Reheater is a part of the boiler which is used for reheating the steam output from the first level of a steam turbine. Reheated steam will again absorb the heat energy from the boiler which is to be used in the next level steam turbine. Reheater is one way to improve the thermal efficiency of the Rankine Cycle.
While designing the re heaters and super heaters, the main parameters to be followed in order to increase the efficiency of the heating include:
- Boiler pressure
- Steam pressure
- Temperature requirement of the process
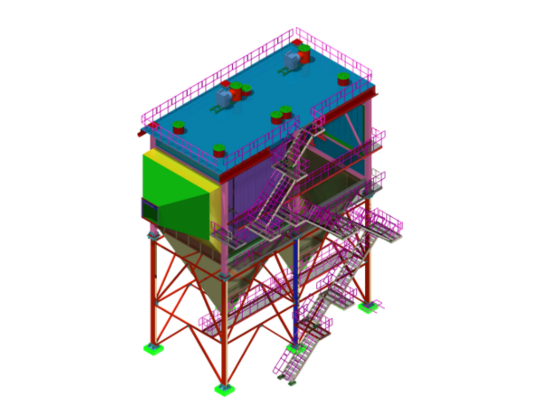
Electrostatic Precipitator (ESP)
In the past, there was no consideration given to dust emissions from industrial plants. Later, governments reacted to reports from environmental protection agencies and the medical industry regarding the harmful effects of particulates that were being released into the atmosphere from industrial plants. Today, typical efficiencies for dust removal from a flue gas system range from between 98% to 99.9%. This process is completed successfully with the help of an Electrostatic Precipitator[ESP].
The purpose of an ESP is to avoid these particulates being expelled into the atmosphere where they can cause pollution. ESPs are installed at many types of industrial plant, but they are most easily identified at thermal power plants where they are installed as part of the flue gas cleaning system. The more efficient design for ESP results in larger resistance in toxic emission, which prevails in an eco-friendly environment.
Automobiles
Automotive design is the process of developing the appearance (and to some extent the ergonomics) of motor vehicles including automobiles, motorcycles, trucks, buses, coaches, and vans. Automotive design in this context focuses primarily on developing the visual appearance or aesthetics of vehicles, while also becoming involved in the creation of product concepts.
Today’s automobiles depend upon mechanical systems that are crucial for aiding in the movement and safety features of the vehicle. On the other side, manufacturers also want their customers to have a good experience while driving and thus aim to improve the handling and the driveability of the vehicle.
In addition to visual appearance and ergonomics, automotive design also involves engineering and technical considerations, such as the selection and integration of mechanical and electronic components, materials, and manufacturing processes.
Overall, automotive design is a complex and multifaceted discipline that encompasses both art and science to create safe, functional, and aesthetically pleasing vehicles that meet the needs and desires of consumers.
Oil And Gas Industry
The world’s dependence on oil and gas is increasing as global economies and infrastructure continue to rely heavily on petroleum-based products. The processes and systems involved in producing and distributing oil and gas are highly complex, capital-intensive, and require precision and recent technologies.
CAD department plays a vital role in enhancing the efficiency of the Oil and Gas industry through most contemporary 3D models for all the machinery involved in the production of oil and gas as resulting products. CAD software is used to create and modify 2D and 3D models of oil and gas equipment such as drilling rigs, pipelines, storage tanks, and refineries. These models can be used to simulate the behaviour of equipment and systems under different operating conditions, allowing engineers and technicians to optimize designs and identify potential issues before construction or implementation.
Turbo Machinery Industry
Turbo machinery is a field that involves the design and manufacturing of machines that transfer energy between fluids and solids, such as turbines, compressors, and pumps. Turbo machines are generally divided into two main categories. The first category is used primarily to produce power. It includes, among others, steam turbines, gas turbines, and hydraulic turbines. The main function of the second category is to increase the total pressure of working fluid by consuming power. Examples of such turbo machines are: Single stage axial flow compressor or pump, mixed flow pump, centrifugal compressor or pump, Francis turbine (mixed flow type), Kaplan turbine and Pelton wheel.
CAD technology has played a vital role in the design and development of turbo machinery, allowing engineers to create efficient and reliable machines that meet the high demands of modern industries. Exemplary design of the turbo machines boosts its efficiency for delivering the output power.

Process Industry
Process industries relies heavily on computer-aided design (CAD) services to design and optimize their equipment and processes. CAD services can help process industries create 2D and 3D models of their equipment, such as reactors, vessels, and piping systems, which can then be used for visualization, simulation, and analysis.
In process industries, CAD services are used for a wide range of applications, including plant layout design, equipment design and optimization, piping and instrumentation diagrams (P&IDs), and process flow diagrams (PFDs). With CAD software, process industries can create detailed models that accurately reflect their equipment and processes, enabling them to identify and address potential issues before they occur.